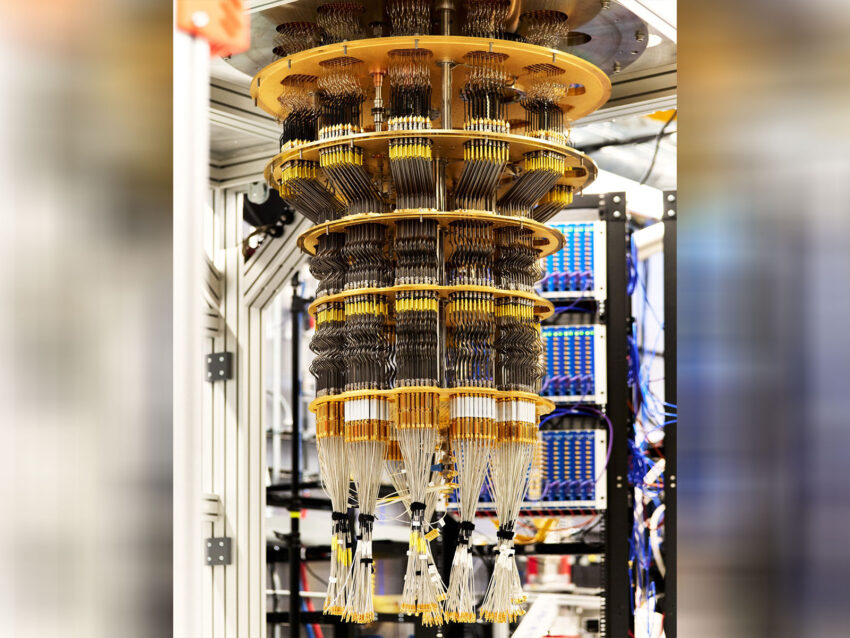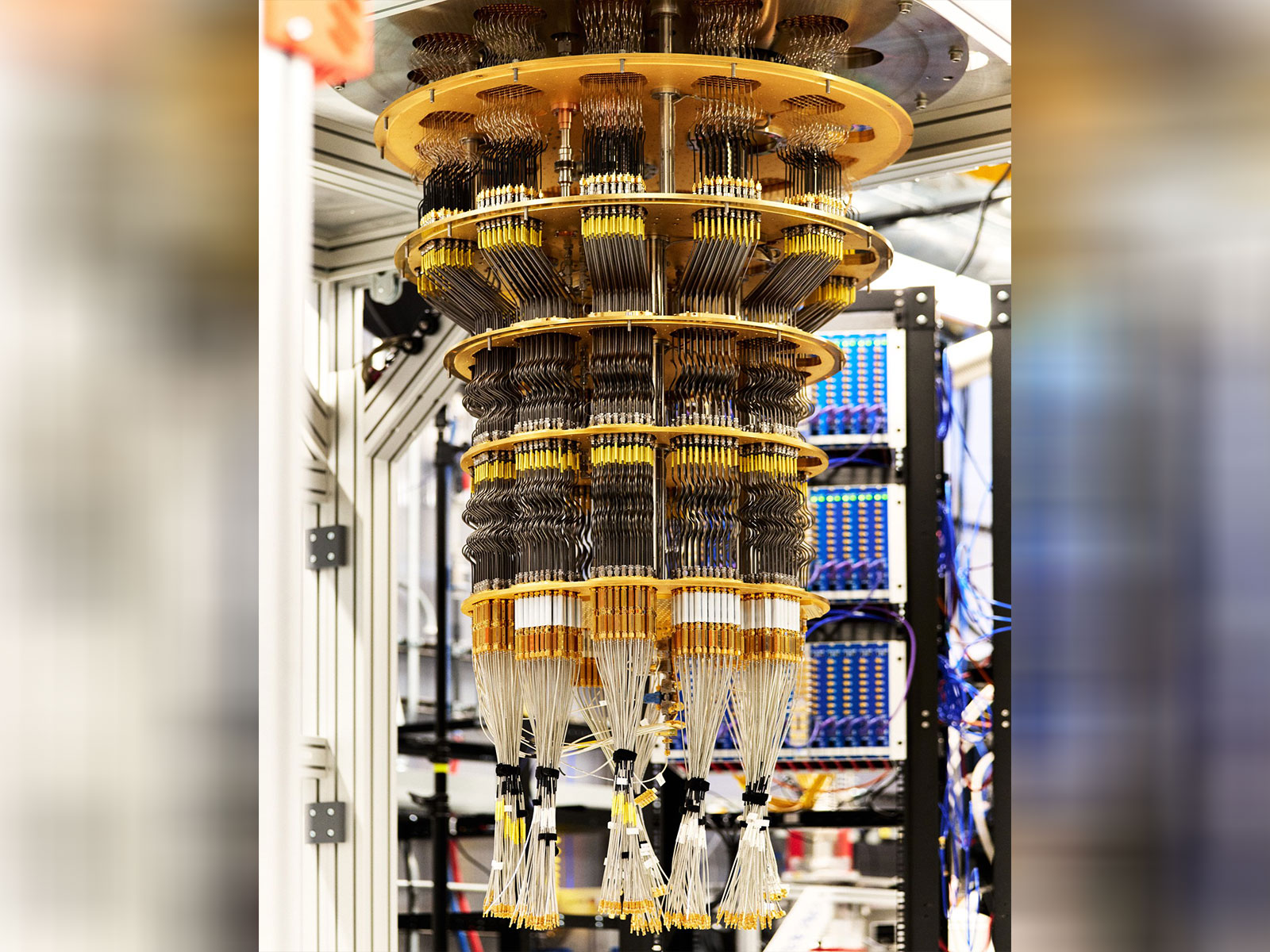
Washington DC [US], October 23 (ANI): In a breakthrough towards reaching the first-ever real-world application of quantum computing, Google Quantum AI’s Willow chip has achieved the “first-ever verifiable quantum advantage”, running its ‘Quantum Echoes’ algorithm at a speed 13 thousand faster than the best classical algorithm in the world’s fastest supercomputer.
Sharing the quantum computing breakthrough on X, Google and Alphabet’s CEO Sundar Pichai highlighted how the new algorithm can “explain interactions between atoms in a molecule using nuclear magnetic resonance” and also pave the way for future discovery in drugs and materials science.
“New breakthrough quantum algorithm published in Nature today: Our Willow chip has achieved the first-ever verifiable quantum advantage. Willow ran the algorithm – which we’ve named Quantum Echoes – 13,000x faster than the best classical algorithm on one of the world’s fastest supercomputers. This new algorithm can explain interactions between atoms in a molecule using nuclear magnetic resonance, paving a path towards potential future uses in drug discovery and materials science,” Pichai said on X.
The result obtained with the Willows Chip is verifiable, meaning it can be replicated by other quantum computers or further experimented with, leading to people getting closer to the first real-world application of quantum computing.
“And the result is verifiable, meaning its outcome can be repeated by other quantum computers or confirmed by experiments. This breakthrough is a significant step toward the first real-world application of quantum computing, and we’re excited to see where it leads”, he said.
The algorithm, along with the chip, can compute the structure of a molecule, according to Google. Google’s Willow quantum chip has been paving the way in understanding quantum computing, as in 2019 it demonstrated that a quantum computer could solve a problem that would take a supercomputer thousands of years. Later on in 2024, the Willow chip showed that errors can be suppressed dramatically, solving a 3-decade-long problem.
The Quantum Echoes is an out-of-order time correlator (OTOC) algorithm, which is a mechanical tool used in quantum computing.
According to Google, Quantum Echoes can be useful in learning the structure of systems in nature, from molecules to magnets to black holes.
In a separate, proof-of-principle experiment, Quantum computation of molecular geometry via many-body nuclear spin echoes demonstrated how the new technique, a “molecular ruler,” can measure longer distances than today’s methods, utilising data from Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) to gain more information about chemical structure.
This is the first time in history that any quantum computer has successfully run a verifiable algorithm that surpasses the ability of supercomputers, Google said, meaning that the result can be repeated on our quantum computer — or any other of the same calibre — to get the same answer, confirming the result.
“This repeatable, beyond-classical computation is the basis for scalable verification, bringing quantum computers closer to becoming tools for practical applications,” Google’s blog read.
The new technique works like a highly advanced echo, sending a carefully crafted signal into our quantum system (qubits on Willow chip), perturbs one qubit, then precisely reverses the signal’s evolution to listen for the “echo” that comes back. (ANI)


